Breakthrough in Pediatric Heart Tumor Detection: VR-Omics Technology Opens New Horizons
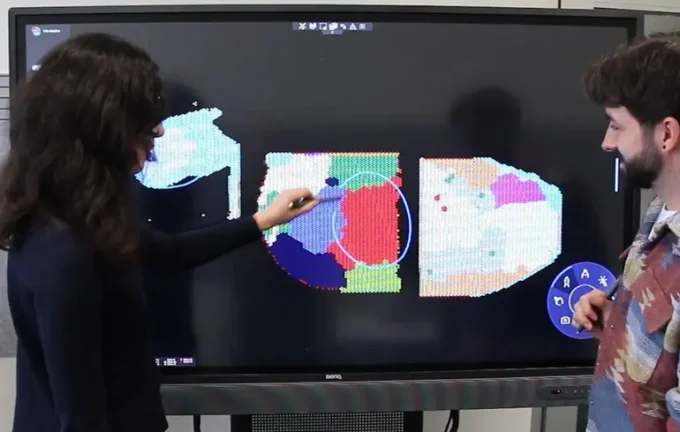
Scientists from Melbourne have made a significant advancement in the fields of pediatric cardiology and oncology by developing an innovative method for detecting and analyzing infant heart tumors using cutting-edge virtual reality and genomics technologies. This revolutionary platform, called VR-Omics, becomes the first of its kind software capable of integrating three-dimensional spatial genomic analysis with immersive virtual reality visualization, thus providing researchers with new tools to understand complex biological processes better. The technology has already demonstrated its effectiveness in studying rhabdomyomas—the most common benign heart tumor in children. By utilizing VR-Omics, a team of researchers collected and analyzed tissue samples from the hearts of three children diagnosed with this tumor type, using specimens obtained from medical institutions in Melbourne. This approach allowed for the discovery of unique cellular behavior patterns previously hidden from conventional methods. Experts highlight that this innovative technology opens exciting new opportunities for investigating the mechanisms underlying the development of childhood tumors. Professor Mirana Ramiálison, a key team member behind VR-Omics, emphasizes that this development enables large-scale genomic data analysis and provides insights into biological processes occurring in rare tissues like cardiac rhabdomyomas. While most cases of rhabdomyoma do not require immediate intervention, some tumors can obstruct blood flow, cause breathing difficulties, arrhythmias, or even lead to heart failure, necessitating surgical intervention with inherent risks for young patients. In this context, VR-Omics has the potential to become a powerful tool for uncovering the causes and characteristics of various pediatric cardiovascular conditions, ultimately paving the way for safer and more effective therapeutic strategies. The research involved scientists from Monash University, Melbourne University, Constance University in Germany, and the Novo Nordisk Foundation’s Center for Cell Medicine. Looking ahead, the team aims to expand the application of this technology across different fields of pediatric genetics and regenerative medicine, contributing significantly to the development of advanced biomedicine, early diagnostics, and personalized treatments for children.

